[err] Memberlist: Failed Fallback Ping: Read Tcp
Consul Toolbelt #1: Example Health

I've moved away from medium due to its content policies.
This is now available here:
.
.
.
.
.
These toolbelt uses aren't plenty to warrant a total Delegate install, but if you lot are already running Consul at that place are some not bad things y'all tin can do with it. This mail is role of a series that highlights some of those uses.
While the front folio of the site does mention failure detection, information technology'south phrased around service discovery and health checks, but in that location is another advantage to Consul's gossip across your fleet. All of a sudden you can now detect bad hosts or hosts with irregular network performance through Serf.
Bare-metallic or in the deject, this is something yous've run across if you've run at scale, and it tin can be difficult to detect even with measuring package loss or other network statistics beyond your armada. The good affair is that the gossip and Serf health in Delegate is doing just that. If you've got some regular network detection tools and metrics this mail service may not be for you, but Consul has an advantage over typical tools, equally it uses correlation from several network points to determine health.
Datadog has bang-up metrics for Consul, but if you commencement seeing some oddities you lot are still going to need to dig into the logs to see what's up. While this mail covers some metrics for Consul, the telemetry provided natively is far more extensive than what is covered here. The approaches hither are mostly for fun and research and intended to illustrate what you can exercise, non how you should do it, in your production infrastructure.
Here's what we'll go over in this post:
- Lifecycle of an instance as viewed by Consul
- Useful log lines from Consul to help detect networking issues and a brief summary of what they hateful
- Using Cloudwatch logs with Consul and generating metrics from them
Important $.25
- If y'all can afford to do so, set your Consul logging level to TRACE or DEBUG. Without these logs it is going to be challenging to fully understand what may be happening.
- Graphing isn't enough, it is only a leading indicator or plenty to point you in the right management. It is often not enough to ready the outcome. I investigated putting this in to Honeycomb.io but for this simple exam but I don't have a manner to interpret these logs out to the supported Honeycomb formats. Information technology could exist a cool utilize case though.
- It'southward important to have all the logs centralized. In a gossip based system you'll need to roughly calculate each nodes individual view of the earth. There is convergence time and other factors where only part of the cluster may remember a node is unhealthy. Flapping tin can exist common. Looking at a single log file tin can be misleading, was it the source or destination node that has a problem? Did information technology become the message from someone else? Consul has great coordinated checks then a single node doesn't make the total decision on failures. Using this information tin can help lead you to locating the source of problems.
- Things are oft not as they seem at first glance. If you lot are new to Consul and y'all install it beyond your infrastructure, yous're likely to find a bunch of failures and issues. It'south easy to blame Delegate issues for this, merely it is more likely Consul will discover issues you didn't know you already had.
- This test doesn't encompass almost everything that can happen and is only a simulation or example of what you can practice with this information. Some of the settings used to simulate network issues are far from perfect.
- I chose to use Docker only for the simplicity of integration with centralized AWS CloudWatch logs. The results here do not require Docker or AWS CloudWatch logs although they practise use them for metrics and centralized logging.
- This will also illustrate how to setup Consul monitoring with metrics from CloudWatch Logs. Other tools tin exercise similar.
- I am not an expert on Delegate or the code, the examples particularly in the source code links don't swoop into great item.
The Test Environment
We volition kick l instances(and iii servers) on AWS of the smallest type possible(t2.nano) equally those are probably our best bet for hit limits or running into issues to illustrate what we are later on in these tests. We volition run the Consul server nodes are slightly larger instances(t2.minor)
Our test surround and setup exercise non mirror production and are for examples simply.
The Setup
Is on GitHub here: https://github.com/pshima/delegate-toolbelt/tree/principal/instance-health
For repeatability the test setup was mostly created with Terraform. For the network simulation this script was used:
Instance Lifecycle
Let's beginning out with something simple — what does it look similar when an instance comes upward and then but disappears due to EC2 wellness issues(simulated 99.9% packet loss in our case).
Our first join effect from the cluster:
2017/08/20 eighteen:39:44 [INFO] serf: EventMemberJoin: ip-10–0–0–190 10.0.0.190 And the last
2017/08/20 eighteen:39:49 [DEBUG] serf: messageJoinType: ip-10–0–0–190 This is interesting to note because it took the entire 53 node cluster only 5 seconds to converge that this node was now alive.
At xx:27:08 we issue the command to drop network traffic and simply over lx seconds afterwards the member has been detected as failed.
2017/08/20 20:28:14 [DEBUG] memberlist: Failed ping: ip-10–0–0–190 (timeout reached) And 17 seconds after the instance is marked every bit failed with 2 peer confirmations of the failure. This is a disquisitional point — the node had to have 3 dissever indications of failure before truly existence marked as failed and this happened about 90 seconds after we dropped traffic. Very cool.
2017/08/twenty 20:28:31 [INFO] memberlist: Mark ip-10–0–0–190 as failed, doubtable timeout reached (2 peer confirmations) The nodes continue to try and contact -190 just at 20:36(13:36 local time) EC2 terminates the case. This was 9 minutes subsequently we started dropping traffic but Delegate detected and marked it for failure in just 1.5 minutes. In a earth where and so many things are measured in minutes just to get enough data information technology is refreshing to encounter health checking make a decision in ane.v minutes later a 17 second detection. Sure beats EC2 health checks.

Examining the Logs
So what are some interesting items in the Consul log entries to help you lot find some of these things?
With the awslogs tool nosotros chop-chop extract all the logs across all 53 nodes locally for analysis. Nosotros could use the straight filtering abilities in awslogs but let's stick with the more than common command line utilities.
% awslogs get consul-toolbelt ALL — start='2h ago' > logs.all Let'southward offset with a unproblematic grep for 'ERR'
Failed Fallback Pings
2017/08/20 xix:24:34 [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: write tcp x.0.0.88:34898->10.0.0.189:8301: i/o timeout Yamux Keepalive Failures
2017/08/twenty 20:18:56 [ERR] yamux: keepalive failed: i/o deadline reached Consul RPC Failures
2017/08/20 20:18:56 [ERR] consul.rpc: multiplex conn accept failed: keepalive timeout from=x.0.0.88:53467
And on to 'WARN'
Refuting Doubtable Letters
2017/08/xx eighteen:43:30 [WARN] memberlist: Refuting a doubtable bulletin (from: ip-10-0-0-52) Memberlist Connectedness Problems
2017/08/xx 20:04:32 [WARN] memberlist: Was able to connect to ip-ten-0-0-76 merely other probes failed, network may be misconfigured
So this is a practiced starting indicate, and it's interesting to note most of the errors and warnings are from memberlist and yamux.
Failed Fallback Pings
These tin can be seen hither: https://github.com/hashicorp/memberlist/blob/bb21552b37d804bddbf4516db355e092f793f164/country.go#L368
According to the code comments, the fallback ping is used in the place of UDP pings when they start failing. This is a cracking feature as UDP traffic tin be by nature unreliable, and so falling dorsum to a TCP ping is pretty sweet. This is a skillful leading indicator of an event and something we may want metrics for.
sendPingAndWaitForAck tin can exist found hither which looks to be using an implementation of https://golang.org/pkg/internet/#Dial
A pretty straight forward network connection. If this isn't working, and fallback to TCP also isn't working, something is wrong.
Yamux Keepalive Failures
Nosotros can observe these here: https://github.com/hashicorp/yamux/blob/d1caa6c97c9fc1cc9e83bbe34d0603f9ff0ce8bd/session.become#L306
According to the comments this is a running ping to keepalive the yamux connectedness. The ping here is used to mensurate the RTT time: https://github.com/hashicorp/yamux/blob/d1caa6c97c9fc1cc9e83bbe34d0603f9ff0ce8bd/session.go#L263
This implementation looks slightly different than the failed fallback pings. It looks like information technology'south sending a SYN packet and calculating the response fourth dimension. This is probably not adept if the destination isn't able to reply to a SYN but information technology also doesn't actually tell us much more the fallbacks. The fallbacks already tell us in that location are connectivity issues across TCP and UDP.
Consul RPC failures
These tin can be establish here: https://github.com/hashicorp/consul/blob/d42c743c84eab122fd7526bca6d7033fd1d179bf/agent/delegate/rpc.go#L135
This appears to exist utilizing the above yamux multiplexer so I don't think that helps us much. The yamux errors are likely correlated.
Refuting Suspect Messages
This tin can be establish here: https://github.com/hashicorp/memberlist/hulk/bb21552b37d804bddbf4516db355e092f793f164/state.become#L1034
So this is a really neat and interesting part of Consul and memberlist. If I get a message from another node that says I am an unhealthy node then I tin can refute that message and say no, here I am and I am good for you.
This is probably one of the more interesting and useful log entries. It shows us that something has gone wrong simply in i way or some other was transient or illustrates network issues between merely a subset of nodes. If this is happening often it most definitely needs to be investigated.
Memberlist connexion problems
So this is close to the failed fallback problems above and only a few lines of code away: https://github.com/hashicorp/memberlist/blob/bb21552b37d804bddbf4516db355e092f793f164/state.become#L393
Simply the interesting case here is we failed to contact the node, but then the fallback channel did work. The more than likely example hither would be when UDP was non working but TCP was, this message would exist useful for detecting when UDP specific issues were happening.
Other Entries
In that location are plenty of other interesting entries in the logs. We did not apply the default ping failure bulletin equally those are likely to occur and we shouldn't care much virtually single ping failures. This is different than the fallback ping failures as at that place were several tries along the way before we reached that stage. No route to host errors were also nowadays when hosts completely died, but we tin can detect that in other means and isn't interesting with the other data.
Metrics from Logs
One of the cracking features of CloudWatch Logs is to be able to easily generate metrics from them. Let's look at what some of the helpful configurations might look similar from the above errors.
Nosotros can create a Metric Filter on our AWS CloudWatch Logs log grouping pretty hands with but the string matching nosotros have above.
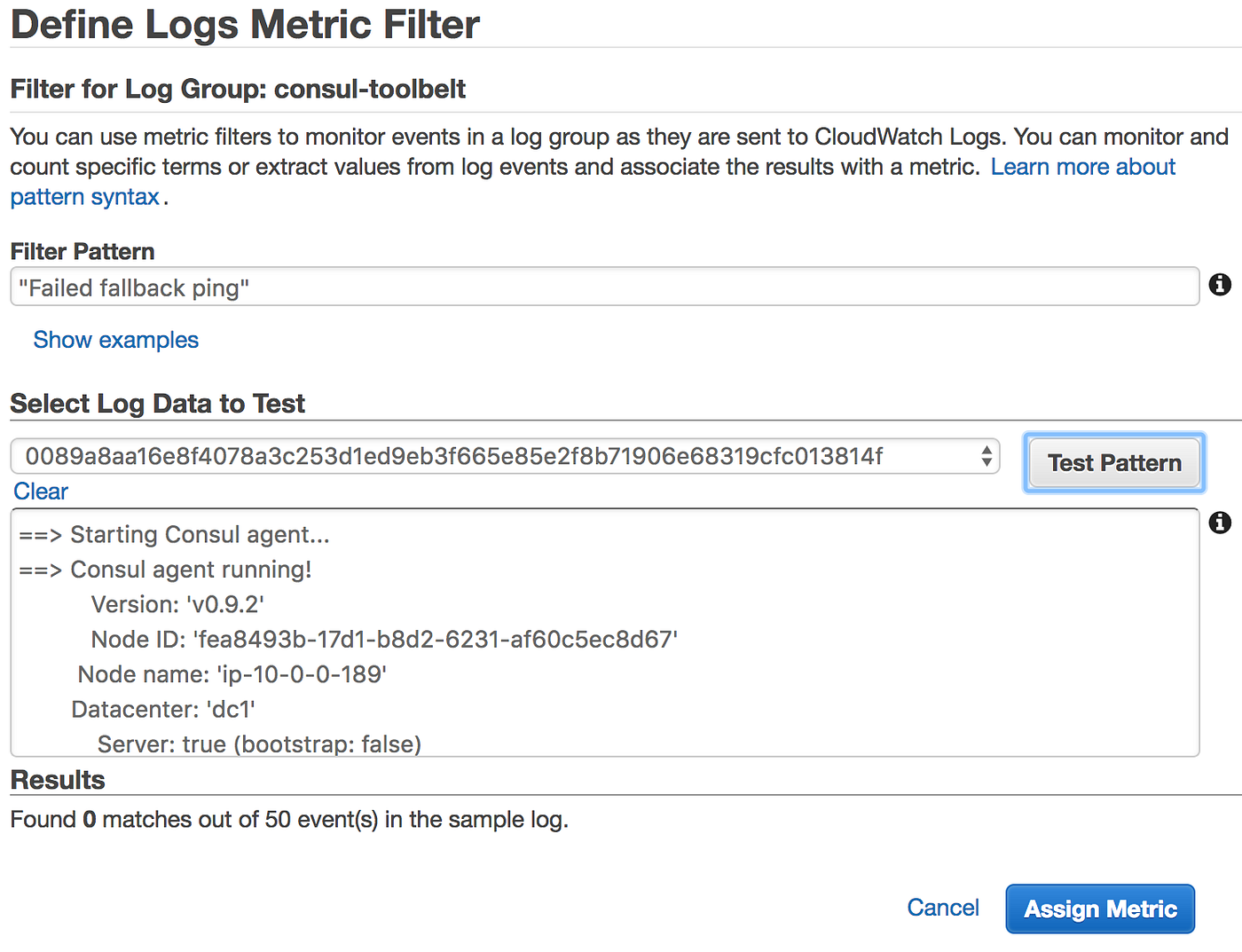
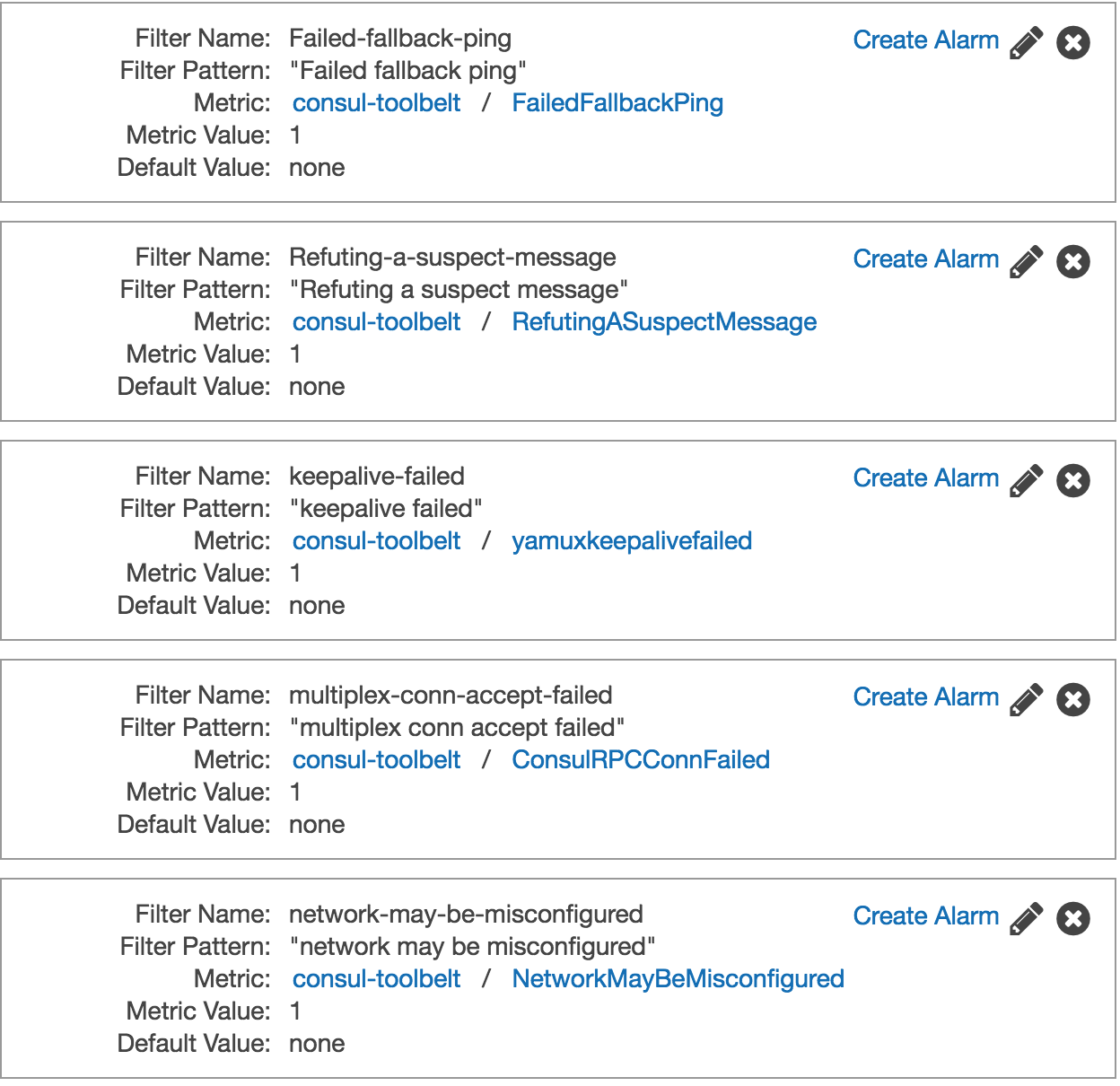
With these setup we could at present also setup some basic alarming if nosotros wanted to, and then with CloudWatch Logs dive in to the log entries and locate what nodes are causing havoc.

Triangulation
With the in a higher place we now have some simple monitoring and debugging nosotros can utilise to detect network problems beyond our armada.
Given the above graph we can see there are over 100 Failed Fallback Pings per minute.
The AWS CloudWatch Logs panel tin can requite us a quick view of the logs

Or the awslogs tool can requite usa quick output of the logs that nosotros can grep beyond.
% awslogs get consul-toolbelt ALL -w | grep 'Failed fallback'
consul-toolbelt 8785f6daffb5f73a9141b70c9a17e572bf93bc1aba96395e80bcbe05afec6432 2017/08/20 21:50:12 [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: read tcp 10.0.0.113:57602->10.0.0.63:8301: i/o timeout
consul-toolbelt 1242f2d1fb4e5412d68541912e4fa25529c231798ea94a70fbcfc38fdc173576 2017/08/20 21:50:xiv [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: read tcp 10.0.0.240:44552->10.0.0.113:8301: i/o timeout
consul-toolbelt 8785f6daffb5f73a9141b70c9a17e572bf93bc1aba96395e80bcbe05afec6432 2017/08/20 21:50:xiv [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: read tcp 10.0.0.113:41928->10.0.0.52:8301: i/o timeout
consul-toolbelt 8785f6daffb5f73a9141b70c9a17e572bf93bc1aba96395e80bcbe05afec6432 2017/08/20 21:50:15 [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: write tcp x.0.0.113:55866->10.0.0.187:8301: i/o timeout
consul-toolbelt 8785f6daffb5f73a9141b70c9a17e572bf93bc1aba96395e80bcbe05afec6432 2017/08/20 21:50:16 [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: read tcp ten.0.0.113:44968->10.0.0.103:8301: i/o timeout
delegate-toolbelt 8785f6daffb5f73a9141b70c9a17e572bf93bc1aba96395e80bcbe05afec6432 2017/08/20 21:50:17 [ERR] memberlist: Failed fallback ping: read tcp 10.0.0.113:50382->10.0.0.134:8301: i/o timeout
With this information technology becomes pretty piece of cake to pick out the outliers using our standard command line utils.
% awslogs get consul-toolbelt ALL --start='5m ago' | grep -o 'ten.0.0.[0-9]*' | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr | head -n 10
199 x.0.0.113
178 10-0-0-113
66 10.0.0.56
58 10.0.0.192
48 10.0.0.83
44 x-0-0-56
37 ten-0-0-192
27 ten.0.0.88
27 10-0-0-83
24 10.0.0.190 10.0.0.113, while under 2 unlike formats is nevertheless any easy choice of our top offender. Since many unlike nodes communicate with this node others will appear throughout the list and we can use this to assist us locate our root crusade(just me with tc).

Summary
I promise this post was useful to you. If you've found other things that take helped you find outlier hosts with Consul, permit me know.
This post covers just some lesser known Consul topics as part of a series called Consul Toolbelt. Tips for people already running Consul.
Source: https://medium.com/@petey5000/consul-toolbelt-1-instance-health-6415cbd4b2fe
Post a Comment for "[err] Memberlist: Failed Fallback Ping: Read Tcp"